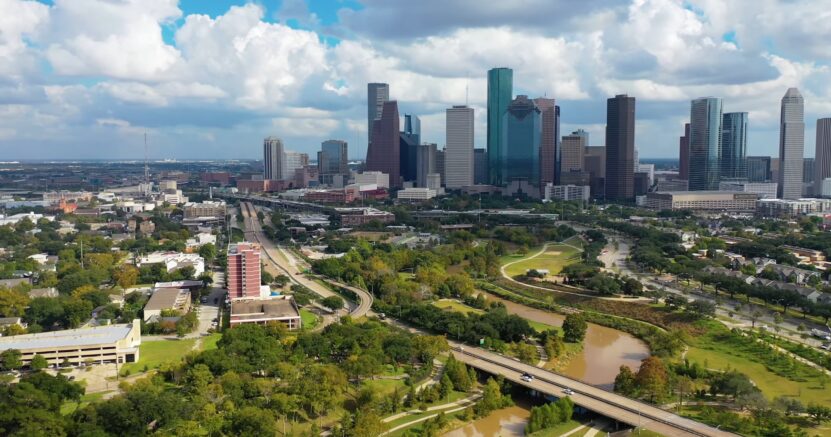
If you’ve ever set foot in Texas, you’ve likely experienced the sweltering heat that engulfs the Lone Star State. With its sizzling temperatures, Texas is often the focal point of discussions surrounding climate and weather. But what exactly is the reason behind the soaring heat in this southern state? In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore the factors contributing to Texas’s torrid temperatures, from its geographical location to climate change’s impact on the region.
Geographical Location: Latitude and Proximity to the Equator
At the heart of the state’s scorching heat lies its geographical location. Situated between the 26th and 36th parallels, Texas is closer to the equator than most states in the U.S. This proximity results in more direct sunlight, leading to increased solar radiation and higher temperatures.
Additionally, Texas’s vast size—stretching over 268,000 square miles—means that it spans multiple climate zones, each with unique weather patterns. From the subtropical climate of the Gulf Coast to the arid conditions of West Texas, these different zones contribute to the state’s overall heat.
Prevailing Weather Patterns: The Influence of High-Pressure Systems
The state’s weather patterns play a significant role in its hot temperatures. The state is often under the influence of high-pressure systems, which tend to bring clear skies and warmer weather. These systems inhibit cloud formation and precipitation, allowing the sun’s rays to heat the ground with little obstruction.
One such high-pressure system is the North American High, a semi-permanent system that influences the weather over much of the central and southern U.S. during the summer months. This system is characterized by sinking air, which suppresses cloud development and rainfall, leading to hotter and drier conditions in Texas.
If you’re curious about extreme winter weather in the United States, there’s a website that lists some of the coldest cities that might surprise you.
Topography: Elevation and Land Features
The topography of Texas also contributes to its heat. Low elevations, particularly in the eastern and southern parts of the state, allow for warm air to be trapped near the ground. The Great Plains in the west are also relatively flat, providing little relief from the sun’s rays.
Moreover, the lack of significant water bodies in Texas means there’s less evaporative cooling to help regulate temperatures. Unlike coastal states, which benefit from sea breezes that moderate temperatures, Texas’s mostly landlocked position causes the state to heat up faster.
Urban Heat Island Effect: The Impact of Urbanization
As Texas’s population continues to grow, so does the urban heat island (UHI) effect. This phenomenon occurs when urban areas experience higher temperatures than their rural surroundings due to human activity and the built environment. Buildings, roads, and other man-made structures absorb and re-radiate heat, contributing to increased temperatures in urban areas.
Texas’s major cities, such as Houston, Dallas, and San Antonio, have experienced significant growth in recent decades, exacerbating the UHI effect. This has caused temperatures in these metropolitan areas to rise even higher than in the rest of the state.
Climate Change: The Role of Global Warming
Climate change is undeniably playing a part in the intensifying heat in Texas. As global temperatures rise due to increased greenhouse gas emissions, Texas has become more susceptible to extreme heat events. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, average temperatures in Texas have risen by approximately 1.5°F since the early 20th century, with the majority of this increase occurring since the 1970s.
Higher temperatures have led to an increase in heatwaves, droughts, and other heat-related events in Texas. In recent years, the state has experienced record-breaking heat, such as the devastating heatwave in 2011, which resulted in widespread power outages, water shortages, and agricultural losses. As climate change continues to progress, Texas is expected to face even more extreme heat events in the future.
Adaptation and Mitigation: Strategies to Cope with the Heat
As Texas grapples with rising temperatures, both adaptation and mitigation strategies are essential to ensure the well-being of its residents and the sustainability of its environment. Some of the steps being taken to address the heat in Texas include:
1. Urban planning and design
To combat the urban heat island effect, cities are implementing various strategies, such as planting more trees, creating green roofs, and using reflective materials on buildings and roads to reduce heat absorption.
2. Water conservation
With increasing temperatures and persistent droughts, water conservation is crucial for Texas. The state is working to improve its water management systems, promote water-saving technologies, and encourage responsible water use among its residents.

3. Early warning systems
Texas is investing in advanced weather monitoring and early warning systems to better predict and prepare for extreme heat events. These systems can help save lives by alerting residents and authorities to impending heatwaves and facilitating timely response measures.
4. Public health initiatives
To protect vulnerable populations from the dangers of extreme heat, Texas is implementing public health initiatives, such as opening cooling centers during heatwaves and providing educational resources on heat-related illnesses.
5. Renewable energy and emission reduction
To combat climate change and reduce its impact on Texas’s heat, the state is investing in renewable energy sources and implementing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What factors contribute to the high temperatures in the Lone Star State?
The scorching heat in Texas can be attributed to its geographical location, prevailing weather patterns, topography, urban heat island effect, and climate change.
2. How does the state’s proximity to the equator affect its climate?
Being closer to the equator means Texas receives more direct sunlight, resulting in increased solar radiation and higher temperatures.
3. How do high-pressure systems impact the weather in the state?
High-pressure systems, like the North American High, bring clear skies and warmer weather by inhibiting cloud formation and precipitation.
4. What is the urban heat island effect, and how does it influence temperatures in cities?
The urban heat island effect is a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures due to human activity and the built environment. This occurs as buildings, roads, and other structures absorb and re-radiate heat, causing city temperatures to rise.
5. What role does climate change play in the region’s rising temperatures?
Climate change is causing global temperatures to rise due to increased greenhouse gas emissions, making Texas more susceptible to extreme heat events, heat waves, and droughts.
6. How are Texans adapting to and mitigating the impacts of the heat?
Strategies include urban planning and design, water conservation, early warning systems, public health initiatives, and investing in renewable energy and emission reduction.
7. Are some parts of Texas hotter than others?
Yes, due to its vast size and multiple climate zones, different regions within the state can experience varying degrees of heat. Eastern and southern parts tend to be hotter due to lower elevations, while urban areas may experience amplified heat due to the urban heat island effect.
8. How can individuals help reduce the heat in their local communities?
By conserving water, planting trees, supporting renewable energy initiatives, and practicing responsible energy use, individuals can contribute to mitigating the heat in their communities.
Final Words
There’s no denying that Texas is a hot state, with its scorching temperatures influenced by a variety of factors, from geographical location and prevailing weather patterns to urbanization and climate change. As Lone Star State faces an increasingly warmer future, it’s vital for policymakers, businesses, and residents alike to work together in developing and implementing strategies to mitigate the heat and adapt to the changing climate. By doing so, Texas can continue to thrive as a vibrant and diverse state, even under the sweltering sun.

